Securing Your Network with Zero Trust Architecture
How Zero Trust Architecture Can Help Secure Your Network
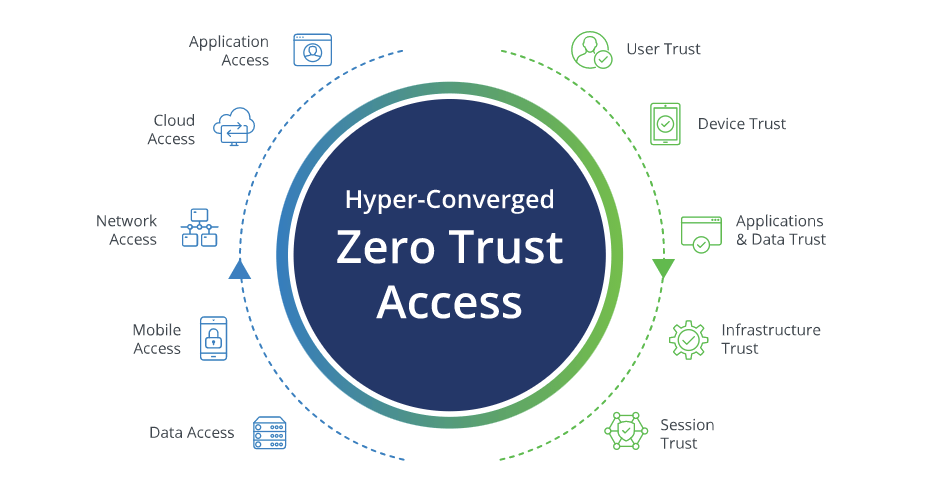
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is an increasingly popular security model that is designed to protect networks from malicious actors. It is based on the principle of “never trust, always verify” and is designed to reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
At its core, ZTA is a security model that assumes that all users, devices, and networks are untrusted and must be verified before access is granted. This means that all users, devices, and networks must be authenticated and authorized before they can access any resources. This is in contrast to traditional security models, which assume that users, devices, and networks are trusted and can access resources without any additional verification.
ZTA also requires that all traffic be monitored and inspected for malicious activity. This means that all traffic must be scanned for malicious code, malware, and other threats. Any suspicious activity must be blocked and reported to the appropriate authorities.
Finally, ZTA requires that all users, devices, and networks be monitored for suspicious activity. This means that any suspicious activity must be reported and investigated. This helps to ensure that any malicious actors are identified and blocked before they can cause any damage.
Overall, Zero Trust Architecture is an effective security model that can help to protect networks from malicious actors. By assuming that all users, devices, and networks are untrusted and requiring that all traffic be monitored and inspected, ZTA can help to reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
The Benefits of Implementing Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) is an increasingly popular security model that is being adopted by organizations of all sizes. ZTA is based on the principle of “never trust, always verify” and is designed to protect networks from malicious actors. By implementing ZTA, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches, protect their networks from malicious actors, and improve their overall security posture.
One of the primary benefits of implementing ZTA is improved security. ZTA is designed to protect networks from malicious actors by verifying the identity of users and devices before granting access to resources. This verification process is known as “zero trust authentication” and is designed to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access the network. By implementing ZTA, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and protect their networks from malicious actors.
Another benefit of implementing ZTA is improved visibility. ZTA provides organizations with greater visibility into their networks by providing detailed logs of user and device activity. This visibility allows organizations to quickly identify suspicious activity and take appropriate action. Additionally, ZTA can be used to detect and prevent insider threats, as it can detect when users are accessing resources they are not authorized to access.
Finally, implementing ZTA can help organizations improve their overall security posture. ZTA is designed to be flexible and scalable, allowing organizations to easily adjust their security policies as their needs change. Additionally, ZTA can be used to integrate with existing security solutions, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, to provide an additional layer of protection.
In summary, implementing Zero Trust Architecture can provide organizations with improved security, improved visibility, and improved overall security posture. By implementing ZTA, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches, protect their networks from malicious actors, and improve their overall security posture.
Understanding the Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is a security model that is based on the principle of never trusting any user, device, or network, regardless of whether they are inside or outside of the organization’s network. This model is designed to protect organizations from cyber threats by ensuring that all users, devices, and networks are authenticated and authorized before they can access any resources.
The core concept of Zero Trust Architecture is that all users, devices, and networks must be authenticated and authorized before they can access any resources. This means that all users must be identified and authenticated before they can access any resources, and all devices must be identified and authorized before they can access any resources. Additionally, all networks must be identified and authorized before they can access any resources.
The goal of Zero Trust Architecture is to reduce the attack surface of an organization by ensuring that all users, devices, and networks are authenticated and authorized before they can access any resources. This is done by implementing a number of security measures, such as multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and network segmentation.
Multi-factor authentication requires users to provide two or more pieces of evidence to prove their identity. This could include a password, a biometric scan, or a one-time code sent to a user’s mobile device. Role-based access control ensures that users only have access to the resources they need to do their job. Network segmentation ensures that different parts of the network are isolated from each other, so that if one part of the network is compromised, the rest of the network remains secure.
Zero Trust Architecture is an important security model that can help organizations protect themselves from cyber threats. By implementing the principles of Zero Trust Architecture, organizations can ensure that all users, devices, and networks are authenticated and authorized before they can access any resources.